Computer Vision Explainability in Safety Surveillance
An explainability framework for safety surveillance, extending Eigen-CAM to YOLOv5 object detection with relevance-based layer selection for bias diagnosis.
Published in Smart Trends in Computing and Communications (SmartCom 2023) as a part of the book series: Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems ((LNNS,volume 650)): link🔗
What is this project about?
This project explores how Eigen-CAM can be applied to YOLOv5 object detection to improve explainability in safety-critical environments. In particular, it focuses on hardhat detection in construction surveillance, where accuracy and trust are vital.
-
Goal:
- Explain YOLOv5’s predictions using Eigen-CAM heatmaps.
- Diagnose whether the model relies on the right visual features (hardhat surface vs. irrelevant cues like faces/background).
- Introduce a relevance-based layer selection strategy to refine explanations for object detection.
Problem Approach
- Modern CNNs (like YOLOv5) are powerful but opaque: their predictions are often black boxes.
- Existing explainability techniques (Grad-CAM, SmoothGrad, etc.) are gradient-based and mainly suited for classification.
- Eigen-CAM is different: it is a gradient-free method that uses singular value decomposition (SVD) on convolutional activations to extract dominant visual features.
-
This project extends Eigen-CAM by:
- Ranking YOLOv5 layers with a relevance score (inside vs. outside bounding boxes).
- Averaging the most relevant layers to produce sharper, more task-specific explanations.
Methodology
-
Detection Module
- Use YOLOv5 to detect objects in a given image.
-
Activation Extraction (Eigen-CAM)
- Collect activation maps from convolutional layers.
- Apply SVD to extract the first principal component → Eigen-CAM saliency map.
-
Relevance-Based Layer Selection (Project Contribution)
- Compute a relevance score = ratio of activations inside bounding boxes vs. outside.
- Rank layers by this score and select the top layers.
- Average these layers’ Eigen-CAM maps for the final explanation.
-
Visualization
- Overlay Eigen-CAM maps on the original image to see which regions drive YOLOv5’s detections.
Applications: Safety Surveillance
- Hardhat Detection – Verify the model’s focus is truly on the hardhat, not worker faces or background noise.
- Bias Diagnosis – Detect when a model relies on spurious features (e.g., skin tone, shadows, clothing).
- Industrial Monitoring – Improve trust in AI systems deployed in construction sites, factories, and surveillance networks.
Why This Approach is Better
-
Eigen-CAM Strengths
- Gradient-free → more stable than gradient-based methods.
- Works with detection models without retraining or modifying the architecture.
- Robust to misclassification: heatmaps aren’t tied to the predicted class score.
-
Project Extension
- Relevance-based layer selection makes explanations more precise for object detection.
- Ensures location-specific insights by focusing on activations inside bounding boxes.
Findings
- Eigen-CAM revealed when YOLOv5 correctly focused on hardhat regions → unbiased detection.
- It also exposed failure cases, where predictions were driven by irrelevant features.
- In benchmark comparisons, Eigen-CAM produced lower error rates than Grad-CAM variants for weakly supervised localization tasks.
Deliverables
- YOLOv5 + Eigen-CAM explainability pipeline.
- Relevance-based layer selection module for object detection.
- Visualization toolkit to generate human-interpretable explanations.
Impact & Implications
- For safety-critical AI: Ensures models are transparent and trustworthy.
- For dataset curation: Helps reveal bias, guiding dataset improvements.
- For explainable AI research: Demonstrates how Eigen-CAM + relevance scoring can extend explainability into object detection tasks.
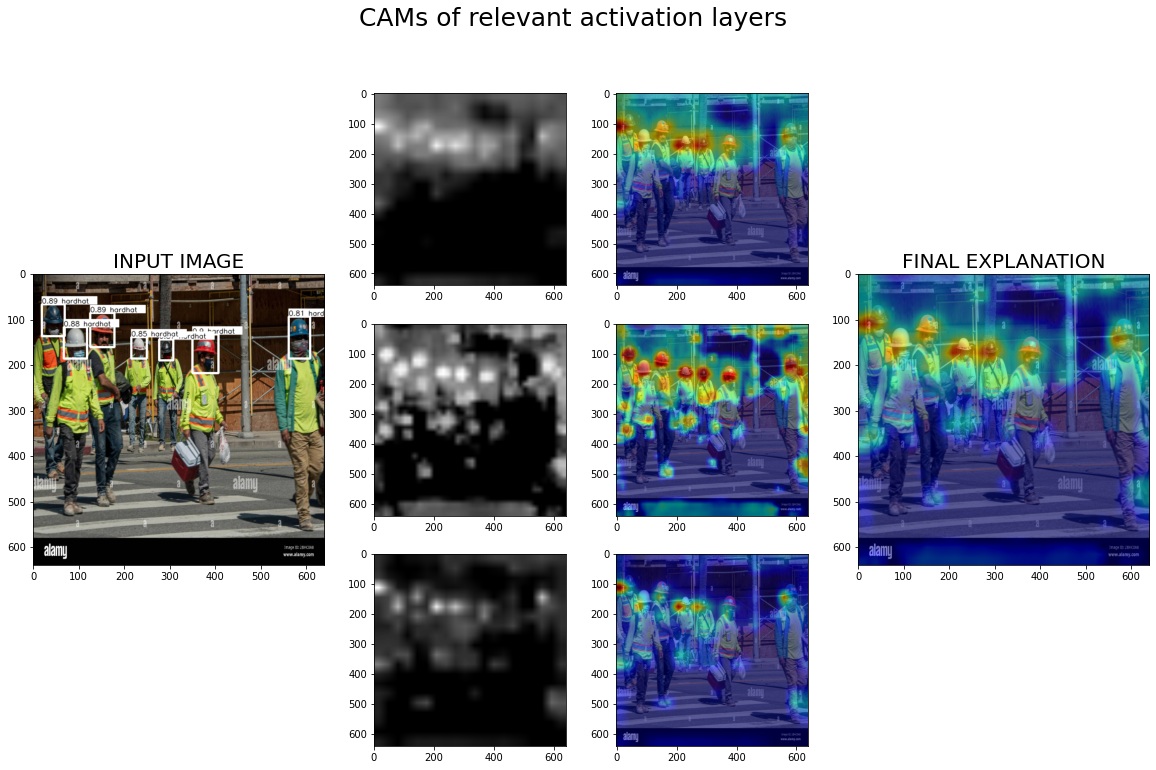
Eigen-CAM explanations for YOLOv5 hardhat detection: the first column shows detections, the middle two columns display saliency maps from the top three most relevant layers, and the final column presents the averaged heatmaps highlighting where the model focuses for predictions.